Essential Nutrients in BARF Raw Diet
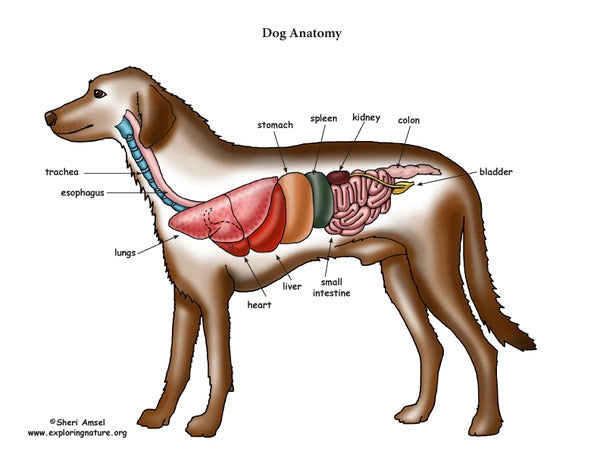
We have created the nutrients information based on the national research council’s guidelines for essential nutrients.
1. Protein
Protein is a structural component of organs, soft tissue, skin, blood, muscle fibre, muscles and connective tissue. It is very important in BARF raw diet for dogs.
Proteins can work as:
-enzymes
-antibodies
-hormones
Proteins are essential for the transportation of molecules throughout the body and extra protein molecules are used for energy.
Protein molecules are also important for conversion into all essential amino acids.
To fulfill the requirement of carbon in nitrogen skeleton.
Essential amino acids:
-Arginine
-Histidine
-Isoleucine
-Leucine
-Lysine
-Methionine
-Phenylalanine
-Threonine
-Tryptophan
-Valine
-Glutamine
-Taurine
How does it absorb in the body?
Protein-rich food enters to stomach (enzyme pepsin and hydrochloric acid releases).
Now partially digested food enters in the small intestine (pancreatic enzyme will release and allow essential amino acids to absorb).
Once essential amino acids are absorbed from the body they use for the creation of tissue proteins, enzymes, albumin, hormones, and other nitrogen-containing compounds.
Source of protein rich food for barf raw diet:
The main source of protein rich food is muscle meat. Raw meaty bones, liver and organs are also considered good sources of protein.
Beef, lamb, chicken and pork are a few examples of animal proteins that all provide all essential amino acids to create a complete diet.
Proteins and amino acids are extremely important for building strong muscle and overall physical strength for your dog.
2. Fat and fatty acids
Fat and fatty acids can not be synthesized in a dog's body so healthy fat and fatty acids are required to function. Fats and fatty acids are important physical activity, source of energy, nutrient absorption and transportation.
Fatty acids and fat are an important part of BARF raw diet for dogs.
Fats contain fatty acids which all have individual roles.
These EFAs include LA, ALA, AA, EPA, and DHA:
-Linoleic Acid (LA)
-Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA)
-Arachidonic Acid (AA)
-Eicosapentaenoic & Docosahexaenoic Acid (EPA/DHA)
The main source of fatty acids:
-Linoleic Acid (LA) - chicken fat, pork fat, chicken skin, hemp seeds and beef fat.
-Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA) - flaxseed, chia seeds and hemp seeds.
-Arachidonic Acid (AA) - chicken thighs, boneless, pork shoulder and ground beef.
-Eicosapentaenoic & Docosahexaenoic Acid (EPA/DHA) - mackerel, salmon, sardines and other raw fish.
3. Fat-soluble Vitamins:
Vitamin A, D, E and K are fat-soluble vitamins.
Vitamins are essential organic substances and are not enough produced by themselves in the body so sufficient sources of these fat-soluble vitamins are necessary to function. Fat-soluble vitamins are extremely important in BARF raw diet for dogs.
Vitamin A: it is an essential vitamin responsible for gene expression, normal vision, reproductive system growth, immunity and tissue formation.
Source of vitamin A is beef liver, chicken liver, beef kidney.
Vitamin D: the primary role of vitamin D in the body of the dog is to enhance the absorption of nutrients in the intestinal tract and also maintain bone deposition balance in calcium and phosphorus.
Source of vitamin D: fish, beef liver.
Vitamin E- vitamin E plays a major role as an antioxidant. It can stop the oxidation of cells. It is also very helpful in gene transportation, modulating immune function.
Source of vitamin E- sunflower seeds.
Vitamin K - it is very useful in bone growth, protein synthesis and blood coagulation functions.
Source of vitamin K: kale, spinach, wheatgrass.
4. Water soluble vitamins
Vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, and B12 are essential water-soluble vitamins.
Each water soluble vitamin has a different role. water soluble vitamins are very important in BARF raw diet for dogs.
Vitamin B1: It is essential to convert carbohydrates into glucose for energy. It also regulates the health of tissue, nerve, muscle and heart.
Source of vitamin B1: beef liver, beef kidney, pork heart, salmon, squash, wheatgrass.
Vitamin B2: Riboflavin is the name of vitamin b2 and it is essential for coenzyme activity, cell growth and development, energy production, metabolism of fat and amino acids.
Source of vitamin B2: Beef kidney, beef liver, chicken liver, pork heart, beef heart.
Vitamin B3: Niacin is a water soluble vitamin that helps to convert carbohydrates into glucose for energy, best stress response and works as a DNA repair. It also helps the metabolism of amino acids and fats.
Source of vitamin B3: Beef, beef liver, beef kidney, chicken, mackerel fish, pork and pork heart.
Vitamin B5: It is useful for coenzyme and protein synthesis. It is also essential for fat, protein and carbohydrate metabolism.
Source of vitamin B5: Beef liver, beef kidney, beef heart, pork heart, chicken liver, salmon, fish, pork, beef, chicken.
Vitamin B6: It is essential for water soluble vitamins and regulates the immune system, nervous system, psychological system. It is essential for the conversion of tryptophan to niacin.
Source of vitamin B6: Salmon, mackerel, beef, pork, chicken, sunflower seeds.
5. Macrominerals:
Minerals are essential components for dogs and can not be produced sufficiently by themselves and must be provided through a balanced diet.
The six essential macro minerals are calcium, phosphorus, sodium, chloride, magnesium, and potassium.
Calcium: Calcium plays an essential role in the structural components of bones and teeth and helps as an ion reservoir. Additionally, calcium enables cells to communicate with hormones and neurotransmitters.
Source of calcium: kale, spinach, bones.
Phosphorus: phosphorus is the second most important mineral required for bones and teeth. Additionally, phosphorus is necessary for DNA and RNA formation and many cellular activities.
Source of phosphorus: Beef, pork and chicken.
Sodium and chloride: These minerals play a major role in maintaining osmotic pressure, maintaining acid-base equilibrium, transmitting nerve impulses, and communicating muscle contractions.
Source of sodium and chloride: kale, spinach and fish.
Magnesium: Magnesium is the third important mineral within the bone and is required in the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. Additionally, magnesium acts as a catalyst for a wide range of enzymes, required for cellular oxidation, a catalyst for most phosphate transfers, and processes neuromuscular activity.
Source of magnesium: Hemp seed, pumpkin seed, sunflower seed, spinach, lettuce and fish.
Potassium: Potassium is essential to maintain acid-base balance, osmotic balance, transmit nerve impulses.
Source of potassium: lettuce, salmon, beef, pork and fish.
These macronutrients are very important for optimal health in a barf raw diet for dogs.
6. Microminerals:
The six micro minerals include iron, zinc, copper, iodine, selenium, and manganese. These minerals cannot be synthesized in quantities sufficient to support normal physiologic function and must be supplied within the diet.
Source of micro minerals: Beef liver, chicken liver, beef spleen, spinach, lettuce, lamb, beef and pork.
Micro minerals are important in BARF raw diet for dogs.